Detector development and testing
High Performance Computing, Modeling and Data Analytics Initiative
The goal of the High-Performance Computing, Modeling and Data Analytics (HPCDA) Initiative is to drive scientific excellence by leveraging the rapidly developing opportunities in computing, materials modeling, machine learning and data analytics, and applying them to neutron scattering data. The initiative forms a crosscut with the other initiatives advancing neutron data analysis across the diverse field of science served by neutron scattering. Focus areas of the initiative are aligned with the 10-year strategic plan for Neutron Sciences [x] covering
- Real Time Data Analysis
- High Performance Computing Materials Modeling
- Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning Applications
An in-depth discussion of efforts related to the entire workflow from data reduction to data analysis and modeling is given in Appendix X. This includes a focused Laboratory Directed Research and Development initiative, the Neutron Data Interpretation Platform Ecosystem, which started in FY2022.
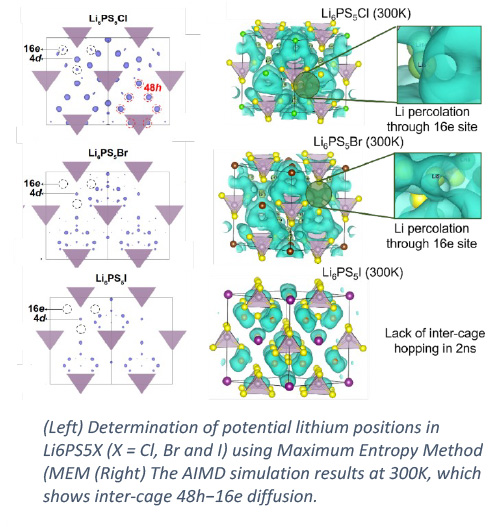
Because of the cross-cutting nature, initiative supported postdocs are frequently joined projects with the other science initiatives. For example, a joined postdoc project with the Materials and Engineering Initiative led to the development of a new way to analysis neutron transmission measurements which may provide a path forward to identify rolling texture components using the transmission technique [2,3]. Another joined postdoc project was mainly focusing on using combined neutron scattering and advanced data analysis/simulation to study rechargeable battery materials, with emphasis on understanding the fast ionic conductivity in various solid-state electrolyte materials [4].The HPCDMA initiative is a critical link between data and computing efforts within NSD and with other ORNL divisions, and to ensure cutting edge analysis, modeling and machine learning developments are integrated across the science strategy of the facilities.
[1] Dessieux, L.L., Stoica, A.D., Frost, M.J. and dos Santos, A.M. (2023A). J. Appl. Cryst. 56, https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576723001346
[2] Dessieux, L.L., Stoica, A.D., Frost, M.J. and dos Santos, A.M. (2023B). J. Appl. Cryst. 56, https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600576723000535
[3] Po-Hsiu Chien, Bin Ouyang, Xuyong Feng, David Mitlin, Jagjit Nanda, Gerbrand Ceder, and Jue Liu, Chem. Mater. in revision.